Model card for Flan-UL2
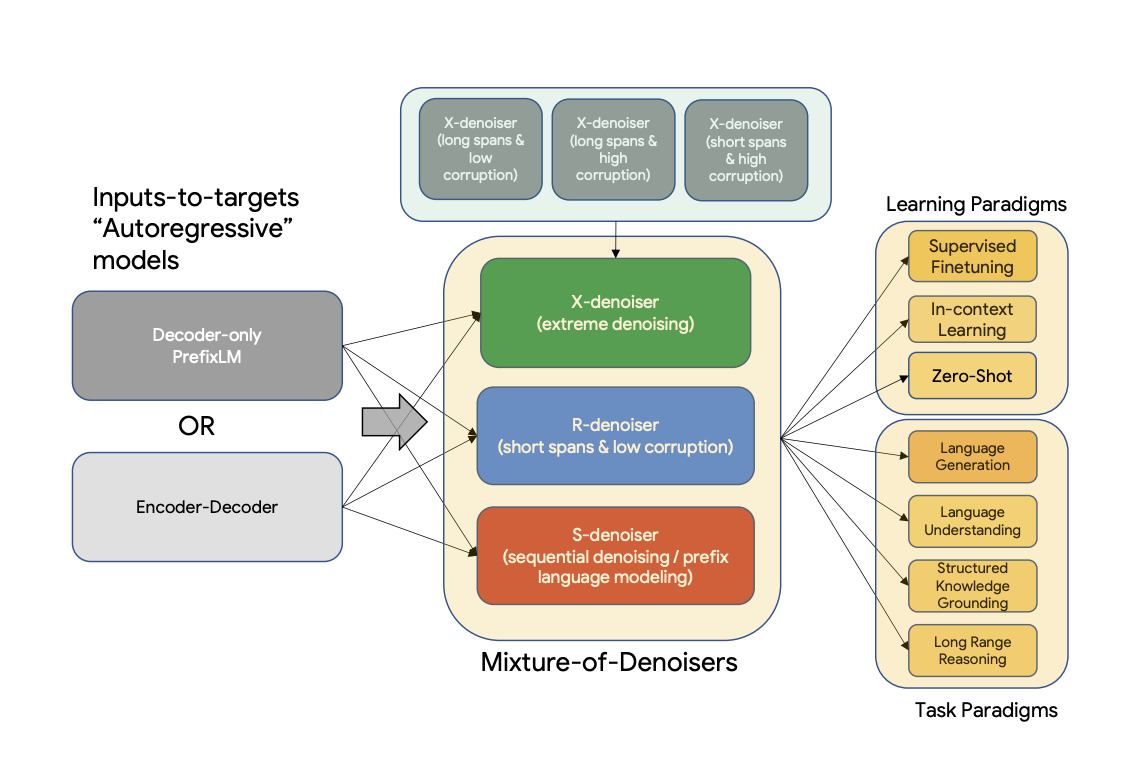
Table of Contents
TL;DR
Flan-UL2 is an encoder decoder model based on the T5 architecture. It uses the same configuration as the UL2 model released earlier last year. It was fine tuned using the "Flan" prompt tuning
and dataset collection.
According to the original blog here are the notable improvements:
- The original UL2 model was only trained with receptive field of 512, which made it non-ideal for N-shot prompting where N is large.
- The Flan-UL2 checkpoint uses a receptive field of 2048 which makes it more usable for few-shot in-context learning.
- The original UL2 model also had mode switch tokens that was rather mandatory to get good performance. However, they were a little cumbersome as this requires often some changes during inference or finetuning. In this update/change, we continue training UL2 20B for an additional 100k steps (with small batch) to forget “mode tokens” before applying Flan instruction tuning. This Flan-UL2 checkpoint does not require mode tokens anymore.
Using the model
Converting from T5x to huggingface
You can use the convert_t5x_checkpoint_to_pytorch.py script and pass the argument strict = False. The final layer norm is missing from the original dictionnary, that is why we are passing the strict = False argument.
python convert_t5x_checkpoint_to_pytorch.py --t5x_checkpoint_path PATH_TO_T5X_CHECKPOINTS --config_file PATH_TO_CONFIG --pytorch_dump_path PATH_TO_SAVE
We used the same config file as google/ul2.
Running the model
For more efficient memory usage, we advise you to load the model in 8bit using load_in_8bit flag as follows (works only under GPU):
# pip install accelerate transformers bitsandbytes
from transformers import T5ForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer
import torch
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("google/flan-ul2", device_map="auto", load_in_8bit=True)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/flan-ul2")
input_string = "Answer the following question by reasoning step by step. The cafeteria had 23 apples. If they used 20 for lunch, and bought 6 more, how many apple do they have?"
inputs = tokenizer(input_string, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_length=200)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
# <pad> They have 23 - 20 = 3 apples left. They have 3 + 6 = 9 apples. Therefore, the answer is 9.</s>
Otherwise, you can load and run the model in bfloat16 as follows:
# pip install accelerate transformers
from transformers import T5ForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer
import torch
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("google/flan-ul2", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/flan-ul2")
input_string = "Answer the following question by reasoning step by step. The cafeteria had 23 apples. If they used 20 for lunch, and bought 6 more, how many apple do they have?"
inputs = tokenizer(input_string, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_length=200)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
# <pad> They have 23 - 20 = 3 apples left. They have 3 + 6 = 9 apples. Therefore, the answer is 9.</s>
Results
Performance improvment
The reported results are the following :
| MMLU | BBH | MMLU-CoT | BBH-CoT | Avg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLAN-PaLM 62B | 59.6 | 47.5 | 56.9 | 44.9 | 49.9 |
| FLAN-PaLM 540B | 73.5 | 57.9 | 70.9 | 66.3 | 67.2 |
| FLAN-T5-XXL 11B | 55.1 | 45.3 | 48.6 | 41.4 | 47.6 |
| FLAN-UL2 20B | 55.7(+1.1%) | 45.9(+1.3%) | 52.2(+7.4%) | 42.7(+3.1%) | 49.1(+3.2%) |
Introduction to UL2
This entire section has been copied from the google/ul2 model card and might be subject of change with respect to flan-ul2.
UL2 is a unified framework for pretraining models that are universally effective across datasets and setups. UL2 uses Mixture-of-Denoisers (MoD), apre-training objective that combines diverse pre-training paradigms together. UL2 introduces a notion of mode switching, wherein downstream fine-tuning is associated with specific pre-training schemes.

Abstract
Existing pre-trained models are generally geared towards a particular class of problems. To date, there seems to be still no consensus on what the right architecture and pre-training setup should be. This paper presents a unified framework for pre-training models that are universally effective across datasets and setups. We begin by disentangling architectural archetypes with pre-training objectives -- two concepts that are commonly conflated. Next, we present a generalized and unified perspective for self-supervision in NLP and show how different pre-training objectives can be cast as one another and how interpolating between different objectives can be effective. We then propose Mixture-of-Denoisers (MoD), a pre-training objective that combines diverse pre-training paradigms together. We furthermore introduce a notion of mode switching, wherein downstream fine-tuning is associated with specific pre-training schemes. We conduct extensive ablative experiments to compare multiple pre-training objectives and find that our method pushes the Pareto-frontier by outperforming T5 and/or GPT-like models across multiple diverse setups. Finally, by scaling our model up to 20B parameters, we achieve SOTA performance on 50 well-established supervised NLP tasks ranging from language generation (with automated and human evaluation), language understanding, text classification, question answering, commonsense reasoning, long text reasoning, structured knowledge grounding and information retrieval. Our model also achieve strong results at in-context learning, outperforming 175B GPT-3 on zero-shot SuperGLUE and tripling the performance of T5-XXL on one-shot summarization.
For more information, please take a look at the original paper.
Paper: Unifying Language Learning Paradigms
Authors: Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
Training
Flan UL2
The Flan-UL2 model was initialized using the UL2 checkpoints, and was then trained additionally using Flan Prompting. This means that the original training corpus is C4,
In “Scaling Instruction-Finetuned language models (Chung et al.)” (also referred to sometimes as the Flan2 paper), the key idea is to train a large language model on a collection of datasets. These datasets are phrased as instructions which enable generalization across diverse tasks. Flan has been primarily trained on academic tasks. In Flan2, we released a series of T5 models ranging from 200M to 11B parameters that have been instruction tuned with Flan.
The Flan datasets have also been open sourced in “The Flan Collection: Designing Data and Methods for Effective Instruction Tuning” (Longpre et al.). See Google AI Blogpost: “The Flan Collection: Advancing Open Source Methods for Instruction Tuning”.
UL2 PreTraining
The model is pretrained on the C4 corpus. For pretraining, the model is trained on a total of 1 trillion tokens on C4 (2 million steps)
with a batch size of 1024. The sequence length is set to 512/512 for inputs and targets.
Dropout is set to 0 during pretraining. Pre-training took slightly more than one month for about 1 trillion
tokens. The model has 32 encoder layers and 32 decoder layers, dmodel of 4096 and df of 16384.
The dimension of each head is 256 for a total of 16 heads. Our model uses a model parallelism of 8.
The same sentencepiece tokenizer as T5 of vocab size 32000 is used (click here for more information about the T5 tokenizer).
UL-20B can be interpreted as a model that is quite similar to T5 but trained with a different objective and slightly different scaling knobs. UL-20B was trained using the Jax and T5X infrastructure.
The training objective during pretraining is a mixture of different denoising strategies that are explained in the following:
Mixture of Denoisers
To quote the paper:
We conjecture that a strong universal model has to be exposed to solving diverse set of problems during pre-training. Given that pre-training is done using self-supervision, we argue that such diversity should be injected to the objective of the model, otherwise the model might suffer from lack a certain ability, like long-coherent text generation. Motivated by this, as well as current class of objective functions, we define three main paradigms that are used during pre-training:
-
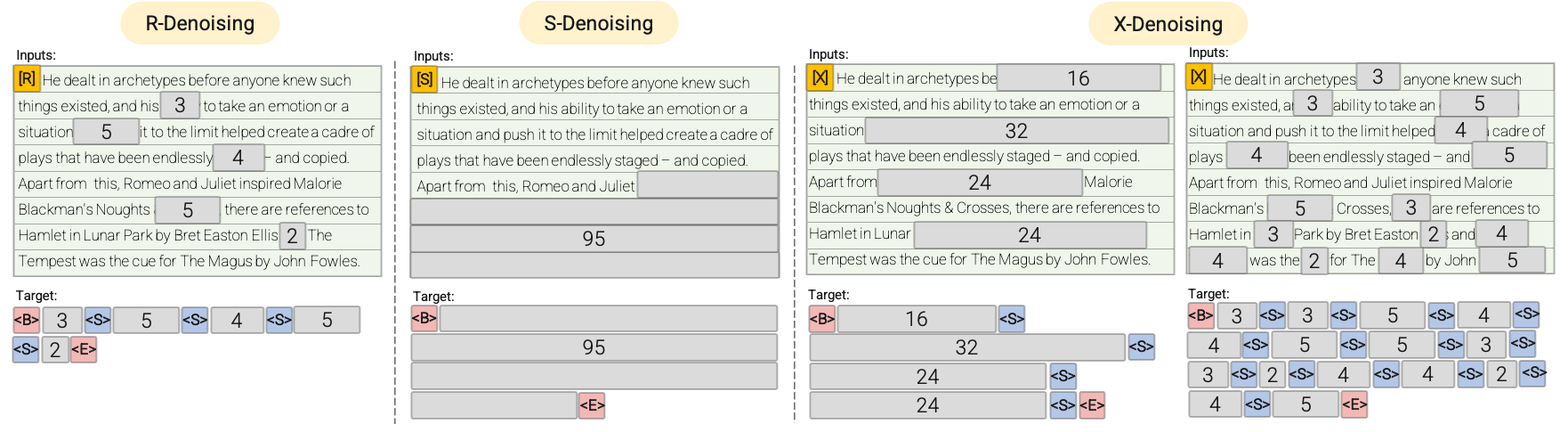
R-Denoiser: The regular denoising is the standard span corruption introduced in T5 that uses a range of 2 to 5 tokens as the span length, which masks about 15% of input tokens. These spans are short and potentially useful to acquire knowledge instead of learning to generate fluent text.
-
S-Denoiser: A specific case of denoising where we observe a strict sequential order when framing the inputs-to-targets task, i.e., prefix language modeling. To do so, we simply partition the input sequence into two sub-sequences of tokens as context and target such that the targets do not rely on future information. This is unlike standard span corruption where there could be a target token with earlier position than a context token. Note that similar to the Prefix-LM setup, the context (prefix) retains a bidirectional receptive field. We note that S-Denoising with very short memory or no memory is in similar spirit to standard causal language modeling.
-
X-Denoiser: An extreme version of denoising where the model must recover a large part of the input, given a small to moderate part of it. This simulates a situation where a model needs to generate long target from a memory with relatively limited information. To do so, we opt to include examples with aggressive denoising where approximately 50% of the input sequence is masked. This is by increasing the span length and/or corruption rate. We consider a pre-training task to be extreme if it has a long span (e.g., ≥ 12 tokens) or have a large corruption rate (e.g., ≥ 30%). X-denoising is motivated by being an interpolation between regular span corruption and language model like objectives.
See the following diagram for a more visual explanation:
Important: For more details, please see sections 3.1.2 of the paper.
Fine-tuning
The model was continously fine-tuned after N pretraining steps where N is typically from 50k to 100k. In other words, after each Nk steps of pretraining, the model is finetuned on each downstream task. See section 5.2.2 of paper to get an overview of all datasets that were used for fine-tuning).
As the model is continuously finetuned, finetuning is stopped on a task once it has reached state-of-the-art to save compute. In total, the model was trained for 2.65 million steps.
Important: For more details, please see sections 5.2.1 and 5.2.2 of the paper.
Contribution
This model was originally contributed by Yi Tay, and added to the Hugging Face ecosystem by Younes Belkada & Arthur Zucker.
Citation
If you want to cite this work, please consider citing the blogpost announcing the release of Flan-UL2.


